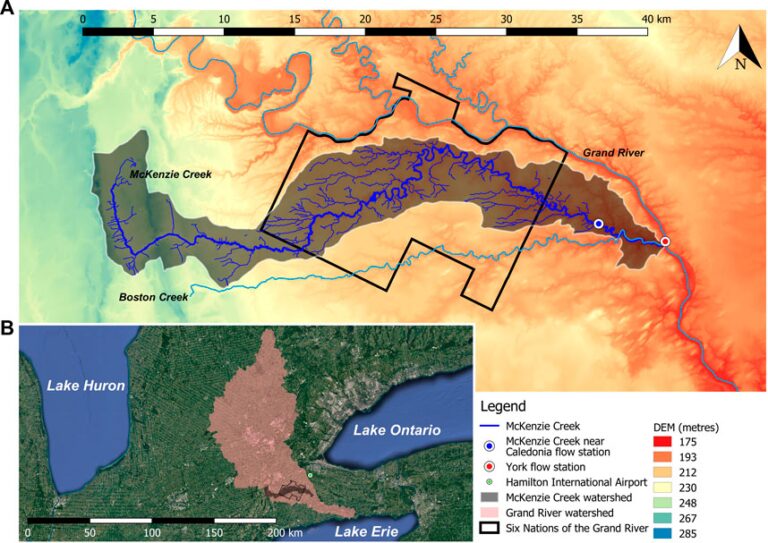
This study examines the impact of climate change on the McKenzie Creek watershed, particularly for the Six Nations of Grand River community in Southern Ontario, Canada. Projections for the region indicate significant increases in temperature (2.3°C to 7.9°C) and precipitation (72–123 mm) by the century’s end, leading to more frequent extreme weather events. These changes threaten streamflow, which is critical for local communities, especially Indigenous populations dependent on smaller streams for water and ecosystem services.
The research utilized the Coupled Groundwater and Surface-Water Flow Model (GSFLOW) to simulate historical (1951-2020) and future (2021-2100) streamflow patterns under two climate scenarios (RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5). Results showed an upward trend in both observed and simulated streamflow, particularly in winter months, while spring and summer flows are projected to decline, raising concerns about water availability during critical agricultural periods. These simulation findings suggest potential increases in winter flooding and summer droughts, highlighting the need for adaptive strategies in water resource management, particularly for vulnerable communities like the Six Nations.
Overall, this study contributes valuable insights for local water resource managers and community planners to prepare for the challenges posed by climate change, with the goal of improving water security and ecosystem resilience in the face of significant climatic shifts.