The article examines the emissions of methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) from ponds and small reservoirs in the Jinjing agricultural watershed of southern China, where these greenhouse gases (GHGs) significantly contribute to global warming. CH4 has a global warming potential 34 times greater than CO2, while N2O is 298 times more potent over 100 years. Despite being only 3.7% of Earth’s non-glaciated surface, small freshwater bodies are substantial sources of GHG emissions, primarily influenced by factors like nutrient levels, water conditions, and biological activity.
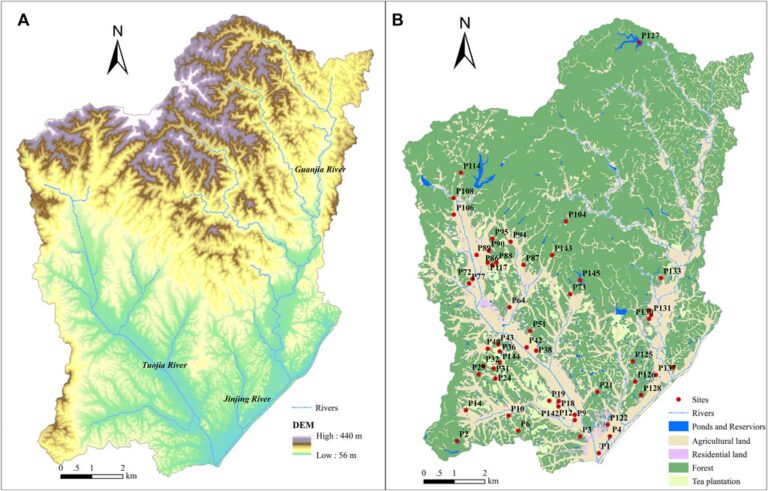
A study sampled 53 ponds over 26 months to assess CH4 and N2O emissions, discovering that emissions were higher in heavily managed ponds (notably fish farms) compared to natural settings, influenced by land use and water quality management. Seasonal variations revealed increased emissions during warmer months linked to rainfall and organic input. The research highlights that eutrophication from agricultural practices exacerbates GHG emissions, implying a need for better management to mitigate climate impacts. The findings underscore the critical role small water bodies play in the global biogeochemical cycle of GHGs, necessitating consideration in climate change assessments.
Overall, the study advocates for ecological management practices to enhance water quality, potentially reducing annual CH4 and N2O emissions significantly and mitigating global warming effects.