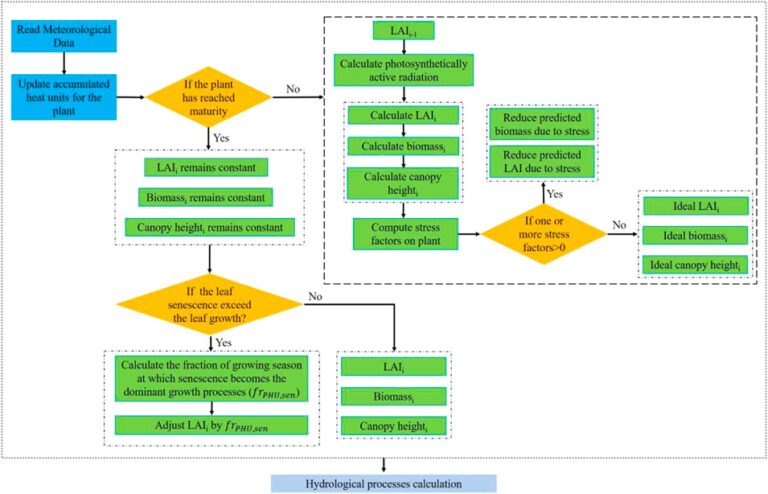
Grasslands are vital ecosystems in arid and alpine regions, influenced by terrain, climate change, and human activities. Different vegetation coverages affect eco-hydrological processes, making it crucial to include vegetation coverage in hydrological models like the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). However, SWAT faces limitations in modeling plant growth due to an oversimplified land use classification and a uniform leaf area index (LAI) calculation that doesn’t account for site-specific variations.
To tackle these issues, the study aims to enhance SWAT’s performance by integrating high-resolution, remotely sensed LAI data based on the Global Land Surface Satellite (GLASS) and Landsat imagery. This leads to capturing the diverse vegetation coverages accurately. The application focuses on the Bayin River watershed, a typical arid region in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, where vegetation comprises primarily grasslands.
Methodologically, land use was classified using Landsat imagery, and the modified model’s performance was validated against site-specific data for streamflow, sediment yield, and evapotranspiration (ET). Results demonstrated that the modified SWAT, which incorporated the high-resolution LAI, significantly improved the simulations of streamflow and sediment yields compared to the original model. Enhanced accuracy in model predictions was also observed in ET simulations, confirming that incorporating high-quality, spatially heterogeneous LAI is vital for effective eco-hydrological modeling.
Overall, this study illustrates the potential of utilizing remotely sensed data to refine hydrological models, particularly in regions undergoing ecological changes due to climate impacts and restoration efforts. The findings highlight the importance of accurate vegetation dynamics in hydrological simulations for effective environmental management and planning.